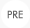보다 지능화되고 있는 웹 방화벽, 그 ‘지능화’의 필요성
성능과 가용성을 중요시 하는 네트워크 분야 보다는 다양한 사용자들의 유형이 표현되고 실제로 개발자들에 의해서 매일 변화가 만들어지는 애플리케이션 분야에서 지능성의 필요는 보안 소프트웨어 생명 자체를 좌지우지할 정도로 너무나 중요한 요소로 자리 잡고 있다. 애플리케이션 보안 중 그 공격 유형이 다양한 웹 애플리케이션 보안 분야와 이를 위한 웹 방화벽에서의 지능화에 대해 살펴보겠다.
공격 패턴을 지능화하여 설정했던 1세대 웹 방화벽
웹 애플리케이션 보안을 담당하는 웹 방화벽은 탄생 초기부터 기존의 보안 장비, 예를 들어 네트워크 방화벽(침입 차단 시스템), 침입 탐지/방지 시스템과는 다른 형태로 만들어 져야 한다는 의견이 일반적이었다. 그 대표적인 이유는 웹 애플리케이션의 특성상 기존의 침입 탐지/방지 시스템에서와 같이 특정한 공격 유형과 패턴, 취약점 패턴 등을 검사하는 것만으로는 공격을 막아낼 수 없기 때문이다.
웹 애플리케이션은 매일 서로 다른 개발자들에 의해서 만들어지고 있고, 지금 이 순간에도 새로운 유형의 취약점이 새로운 애플리케이션에 알게 모르게 만들어지고 있는 것이 현실이다. 이러한 형태에 대한 대응을 위하여 제시된 웹 애플리케이션 보안의 핵심 키워드가 바로 ‘Positive Security Model’이다. Positive Security Model을 갖는 웹 방화벽 구현을 위하여 기존의 보안 장비들의 공격 대응 방식인 Black List 관리 방식에 더하여 White List 관리 방식을 도입하여 Positive Security Model을 구현한 웹 방화벽들이 시장에 선보이게 되었다.
이러한 1세대 웹 방화벽의 경우 관리자는 보안 정책 구현을 위하여 Black List와 White List로 관리되는 패턴 데이터베이스를 직접 등록하거나 관리하는 노력이 필요하다. 여기서 웹 방화벽의 지능은 관리자가 등록 및 편집하는 패턴 정보(일종의 Signature)에 의해 결정된다. 웹 방화벽 자체가 지능이 있다기보다는 웹 방화벽은 패턴 매칭 엔진을 탑재하고 있고, 관리자의 인간 지능이 패턴을 최적화하여 등록해야 한다.
이러한 1세대 웹 방화벽은 기존의 고성능 패턴 매칭 엔진을 보유한 기업에서 쉽게 웹 방화벽을 출시할 수 있는 방식이었다. 기존의 침입 탐지/방지 시스템과는 다르게 웹 애플리케이션에 대한 공격을 패턴 데이터베이스 업데이트만으로 방어할 수 없다는 인식에서 White List 방식을 도입했지만, 관리자가 직접 설정해야 하는 불편함은 White List 방식을 실제적으로 사용하지 않게 만들고, 현실적으로 Black List 만으로 웹 공격들을 막는 일을 초래했다.
이러한 운영 방식은 웹 방화벽을 무용지물로 만들거나 또는 오탐으로 인한 웹서비스 방해물로 전락시키게 되어, 보안 시장에서는 웹 방화벽은 오탐이 많아서 웹서비스에 영향을 많이 주는 제품 또는 다양한 웹 공격들, 대표적으로 SQL Injection과 같이 변이가 많은 공격들을 제대로 막지 못 하는 제품으로 누명을 쓰게 된다.
자동 학습 지능을 탑재한 2세대 웹 방화벽
보안 시장에서 웹 방화벽의 가능성을 보여준 것은 White List에 대한 관리자의 설정 행위, 즉 운영을 자동화한 2세대 웹 방화벽의 역할이었다. 2세대 웹 방화벽은 관리자가 직접 White List를 설정해야 하는 불편함을 자동 학습 기능으로 제공하여 관리자가 실제적으로 White List를 현실에 맞게 사용할 수 있는 방안을 제공했다.
White List는 매우 강력한 보안 기능임에도 불구하고 현재 애플리케이션에 적합한 정책이 설정되지 않으면 애플리케이션을 사용할 수 없게 만드는 치명적인 반대 효과가 나타나기 때문에 1세대 웹 방화벽에서는 관리자가 수동 설정을 하는 많은 수고를 들이거나 White List 방식을 대부분 사용하지 않게 되는 결과를 낳았다. 하지만 2세대 웹 방화벽에서는 이를 자동으로 학습하여 관리자가 현재 애플리케이션에 적합한 보안 정책을 수동으로 만들지 않고 자동으로 얻어낼 수 있는 기능을 제공했다.
결국 2세대 웹 방화벽은 학습 기능의 지능이 웹 보안을 원하는 관리자가 사용 가능한 효과적인 수준인가가 제품의 품질을 결정하게 되었다. 어떤 제품은 최소 2주간의 학습기간을 거쳐야만 학습이 가능한 제품이 있는데, 이 경우 국내에서와 같이 웹 애플리케이션이 매일 매일 변화되는 환경에서는 현실적으로 사용이 어려운 단점이 있다.
또한 학습 지능이 아무리 좋다고 하더라도 관리자에게 검증을 받지 않는 정책을 바로 적용하는 것은 White List의 성격 상 웹 애플리케이션 서비스 자체의 장애로 까지 이어질 수 있기 때문에 관리자의 수동 정책 설정보다는 수월해 졌지만, 정책 설정에 관리자가 매우 깊게 개입해야 하는 것은 2세대 웹 방화벽의 여전한 특징이다.
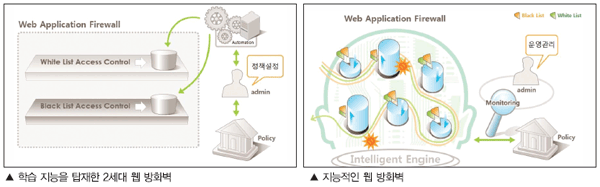
새로운 개념의 지능을 탑재한 웹 방화벽
2세대 웹 방화벽이 고도의 기술 개발과 지능 개발을 통하여 매우 현실적인 웹 방화벽을 만들어 낼 수 있을 것이라는 기대도 있지만 웹 애플리케이션 특성에 초점을 맞춘 새로운 개념의 지능을 탑재한 웹 방화벽에 대한 기대는 클 수밖에 없다. 기존의 2세대 웹 방화벽 역시 기존의 1세대와 같이 Black List와 White List를 계층적으로 결합한 형태로 고성능 패턴 매칭 엔진을 이용하여 Black List는 빈번하고 빠른 패턴 업데이트를 필요로 하고 White List는 현재 보호하고자 하는 웹 애플리케이션을 최대한 모델링 하겠다는 취지에는 큰 변화가 없기 때문이다.
지능적인 웹 방화벽은 Black List와 White List의 물리적인 결합이 아닌 웹 애플리케이션과 웹 공격에 대한 최적의 방어 엔진을 설계하고 엔진 내부의 기능이 자연스럽게 Black List와 White List의 결합, 그리고 Positive Security Model의 구현의 포함하고 있는 형태이다. 이러한 도전을 진행한 제품이 필자의 회사에게 개발한 WAPPLES이라는 웹 방화벽이다. WAPPLES이 지능형 웹 방화벽의 정답은 될 수 없겠지만 웹 애플리케이션 보안을 기존의 방어 기술의 결합이 아닌 새로운 시각에서 접근했다는 점과 관리자 관점에서의 운영성을 반영하여 지능화한 노력은 주목할 만할 점이다.
‘지능화’는 보안 제품의 숙명
보안 제품을 만드는 사람들이 각자 자신의 위치에서 지능화에 최선의 노력을 기울이는 것이 지금의 보안 환경에서는 당연한 일이 된 듯 하다. 웹 방화벽이 웹서비스의 대중화와 확대에 따라서 더욱 많은 관심을 받는 상황에서 WAPPLES에 대한 시장에서의 평가가 웹 방화벽 시장에서 ‘지능화’에 대한 노력이 얼마나 성공을 거둘 것인가로 주목을 받을 만한 가치가 있다. 이제는 지능화된 보안 제품만이 고객의 선택을 받을 수 있고 실질적으로 고객에게 도움을 줄 수 있다는 점에서 ‘지능화’는 보안 제품의 숙명이라 하겠다.
<글 : 김덕수 펜타시큐리티시스템 보안기술연구소장(dskim@pentasecurity.com)>
'컴맹의 컴퓨터 이야기 > 동향' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [펌] 봇넷/DDoS/컨피커, 그 다음은? (0) | 2009.06.23 |
|---|---|
| [펌] 웹 애플리케이션 보안 VS 웹 사이트 컴플라이언스 (0) | 2009.06.17 |
| [웹] 웹 2.0 보안: 소셜 웹 사용시 주의 사항 (0) | 2009.06.11 |
| [펌] 공공기관 망분리로 보안 및 관리수준 한 단계 상승 (0) | 2009.06.10 |
| [펌] 논리적/물리적 보안 융합 : 하나의 보안 시스템으로 (0) | 2009.06.09 |